Van Der Waals Equation Used to Describe Real Gases
The excluded volume of gas particles and attractive forces between gas molecules. This is for one mole.

Non Ideal Gases And The Van Der Waals Equation Youtube
One of the most useful equations developed to predict the behavior of real gases was proposed by the Dutch scientist Johannes van der Waals 1837-1923.

. The van der Waals equation is only one of many equations of state for real gases. The ideal-gas equation predicts that the pressure of a gas is 𝑃 𝑛 𝑅 𝑇 𝑉 𝑖𝑙 𝑔 Van der Waals recognized that for a real. The van der Waals equation is an equation of state that corrects for two properties of real gases.
Van der Waals equation is an attempt to make corrections to real gases that do not exhibit ideal behavior. Is the volume of the container and a. When we deal with real gases at normal or elevated pressures the observations show deviations from ideal behavior and hence we cannot use ideal gas equation.
For classical ideal gas we have pV NT and so р kBT N ñ V 8 where N is the number of particles in a volume V and thus ñ NV is the number density of particles in the gas ie number of gas particles per volume. It takes into consideration the molecular size of the gas-particle and. This law predicts the properties of real gases by describing particles of non-zero volume governed by pairwise attractive forces.
The van der Waals equation of state is written as. Which of the following statements explain why the van der Waals equation must be used to describe real X. For real gases we make two changes by adding a constant to the pressure term P and subtracting a different constant from the volume term V.
It is an equation used to describe the behaviour of gases in conditions of temperature T and pressure P over a wider range than for ideal gases for a volume V occupied by n moles. The Van der Waals equation is the next one. A is the experimental value that represents the intermolecular fores of the vapor.
That means pressure of real gas is less than the ideal gas. Answer 1 of 2. Van der Waals equation is an equation relating the relationship between the pressure volume temperature and amount of real gases.
P - a V² V - b R T a and b are constant and depend upon nature of gas involved. PV n R T. To show this the Van der Waals equation is first rearranged so that the pressure p can be represented as a function of the volume V m.
P an2 V 2V nb nRT P a n 2 V 2 V n b n R T. Ideal gas equation is obeyed by non ideal gases at very low pressures. 1 The ideal gas law is the following.
Van der Waals A modification to the ideal gas law that can be used to correct for the intermolecular forces and molecular volumes in determining the moles of gas present in the system. Describe the type of gaseous molecules that are most susceptible to nonideal behavior. Students should be given time to work through the full activity and any groups that finish early can repeat the real gas section using a different equation of state eg.
The van der Waals equation modifies the ideal gas law. PnRT V-nb-an2 T Vnc2. We do not go into deriving van der Waals equation now but we can express it as p a n2 V 2V nb nRT 3 3 p a n 2 V 2 V n b n R T.
The Van der Waals equation is the equation of state of real gases named after its discoverer the Nobel physics prize winner Johannes Diderik Van der Waals. The equation is meant to describe real gases better. These are used to as corrections of the ideal law equation.
P a nV2 Vn b nRT Here a is a constant that depends on the type of gas and b is also a constant that gives the volume per mole of gas occupied by the molecules of gas. The ideal gas law equation is an equation used for analyzing ideal gases. The caloric-state equation for nonideal gases is obtained from the general result 822 in the following form 1347 U k T 2 T ln Z N V or in terms of the free energy F kT ln ZN 1348 U k T 2.
For a real gas containing n moles the equation is written as. These generally take account of higher-order nonlinear attractive forces and require the use of more empirical constants. Is the gas constant T.
The constants a and b represent the magnitude of intermolecular attraction and excluded. Assessment Students turn in one handout per group and the file with the corresponding plots at the end of class. The Van der Waals equations can be used not only to describe the behavior of real substances in the gas phase but also to explain the phase transition from the gaseous state to the liquid state at high pressures.
Here we see P of previous gas equation is replaced by P - a V². P a n 2 V 2 V n b n R T. P an2 V.
The Van der Waal equation can be given as below. This is called van der Waals equation. P V 2a VbnRT where P is pressure V is volume R is universal gas constant and T is absolute temperature.
The van der Waals equation is frequently presented as. According to the kinetic molecular theory that defines an ideal gas no ideal gases exist in nature only real gases. Is the temperature P.
Is the measured pressure V. Is the moles of the gas R. More elaborate equations are required to describe the behavior of gases over wider pressure ranges.
The molecular attractions between particles of gas decreases the pressure. Van der Waals equation is a modification of the original ideal gas law. The van der Waals equation is the thermal-state equation for nonideal gases.
Interactions between gas molecules reduces the temperature of the gas in the sample Y. Lets play with the van der Waals equation of state again. PVRT versus pressure for 1 mol of nitrogen gas at three different temperatures.
P n²aV²V-nb nRT PVTR have the same meanings as other equation. The van der Waals equation for real gases recognizes that A the molecular atrractions between paritcles of a gas decreases the pressure exerted by the gas B the non-zero volumes of gas particles effectively decrease the amount Chemistry. The new equation looks like this.
The non-zero volumes of gas particles effectively decrease the amount of empty space between them Z. In chemistry and thermodynamics the Van der Waals equation or Van der Waals equation of state is an equation of state which extends the ideal gas law to include the effects of interaction between molecules of a gas as well as accounting for the finite size of the molecules. Van der Waals equation for real gases is the corrected form of ideal gas equation which includes the effects of intermolecular forces of attraction and space occupied by gas molecules.
It is due to mutual attraction between any two gas molecules.

Real Gases And Van Der Waals Equation Youtube

Van Der Waals Equation Real Gases Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Significance And Limitations Of Van Der Waals Equation Qs Study
Why Does The Value Of Ideal Gas Equation And Van Der Waals Gives Different Answers Quora
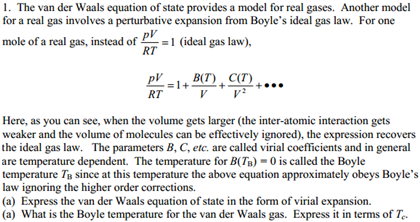
Solved The Van Der Waals Equation Of State Provides A Model Chegg Com

Real Vs Ideal Gases Van Der Waals Explained For General Chemistry Youtube
How Is It Possible For Ideal Gas To Have Low Pressure While According To Van Der Waals Equation Real Gases Have Lower Pressure Quora
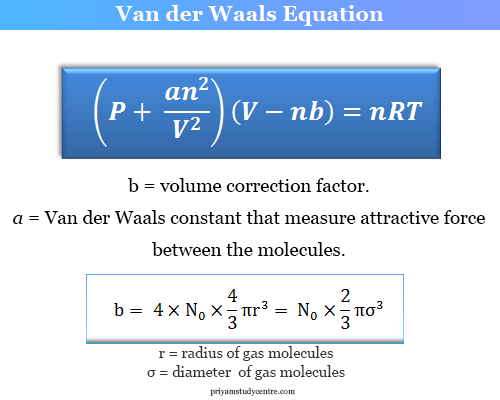
Van Der Waals Equation Derivation Formula Units Chemistry

Real Gases Factors That Cause Deviation From Ideal Behavior 11 6 At High Pressure Molecules Are Close Together And Individual Volume Becomes Significant Ppt Download

The Van Der Wall Equation For 1 Mole Of A Real Gas Is P A V 2 V B Rt Where P Is The Pressure V Is The Volume T

Gas Laws Which Gas Is Easier To Compress The Ideal Gas Or A Real Gas Chemistry Stack Exchange
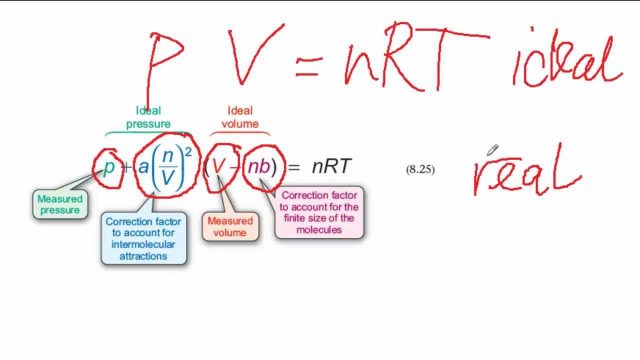
The Van Der Waals Contribution To The Mystery Of The Gas Metal Interaction Mapping Ignorance

Write The Vander Waals Equation

Chapter 8 Real Gases Ppt Video Online Download
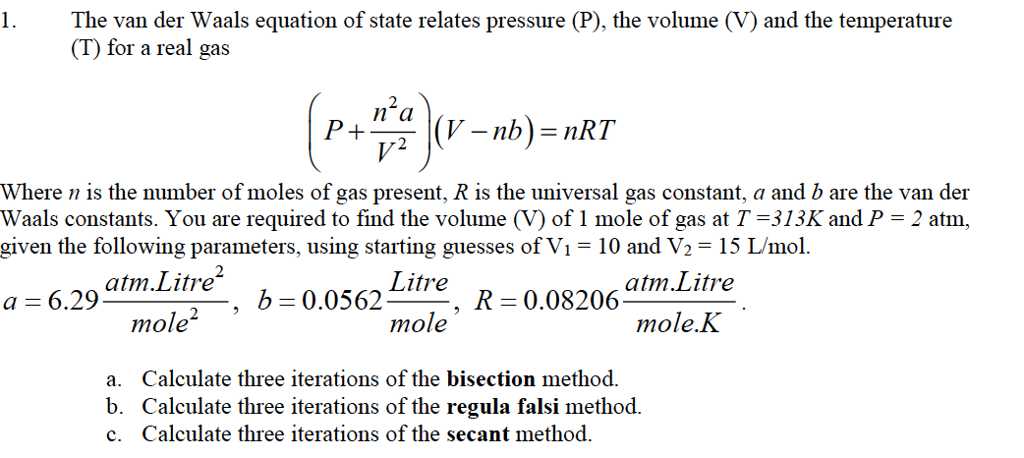
Solved 1 The Van Der Waals Equation Of State Relates Chegg Com

Van Der Waals Equation For Real Gases Doesn T Make Sense R Chemhelp
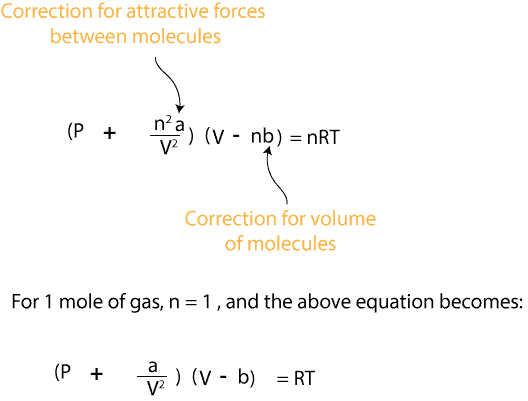
Van Der Waal S Equation And The Significance Of The Constants A And B

Van Der Waals Equation Flashcards Quizlet
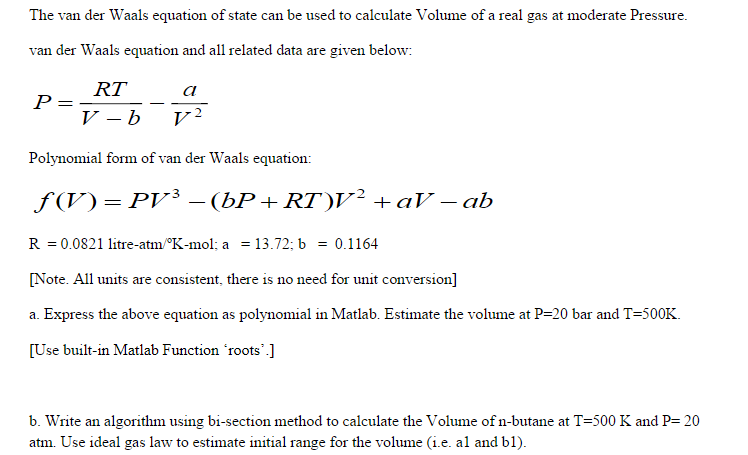
Solved The Van Der Waals Equation Of State Can Be Used To Chegg Com
Comments
Post a Comment